Findings From the REVEAL Registry*
REVEAL was a US-based, observational registry involving 55 academic- and community-based treatment centers. 3515 patients enrolled between March 2006 and December 2009.4
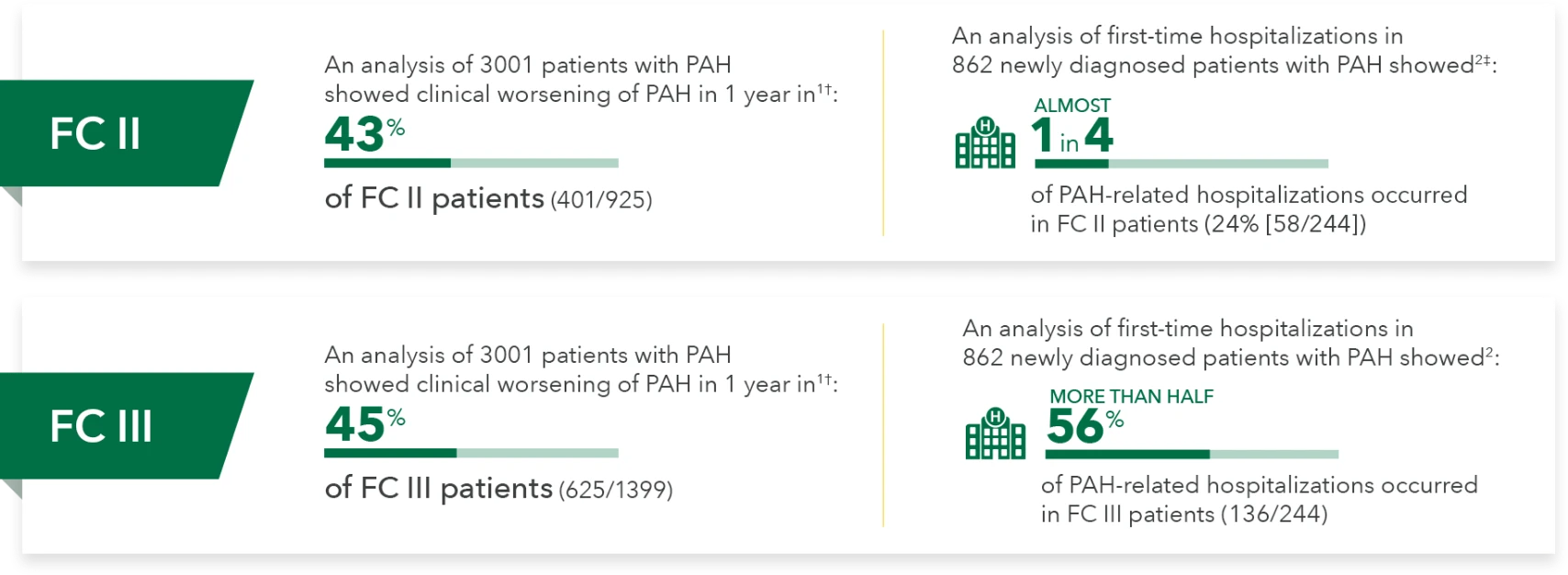
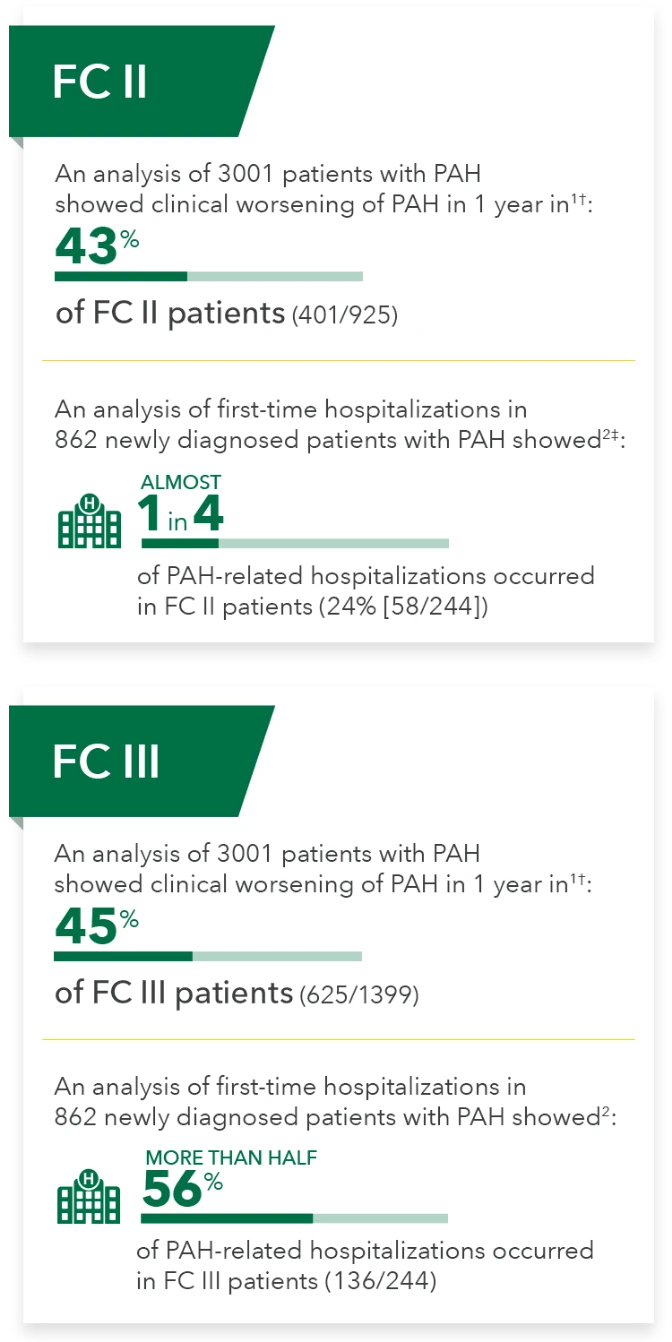
An analysis of 3001 patients with PAH showed clinical worsening of PAH in 1 year in 1†:
43%
of FC II patients (401/925)
An anaylsis of first-time hospitalizations in 862 newly diagnosed patients with PAH showed 2‡:
of PAH-related hospitalizations occured in FC II patients(24% [58/244])
An analysis of 3001 patients with PAH showed clinical worsening of PAH in 1 year in 1†:
of FC III patients(625/1399)
An analysis of first-time hospitalizations in 862 newly diagnosed patients with PAH showed2:
og PAH-related hospitalizations occured in FC III patients (136/244)